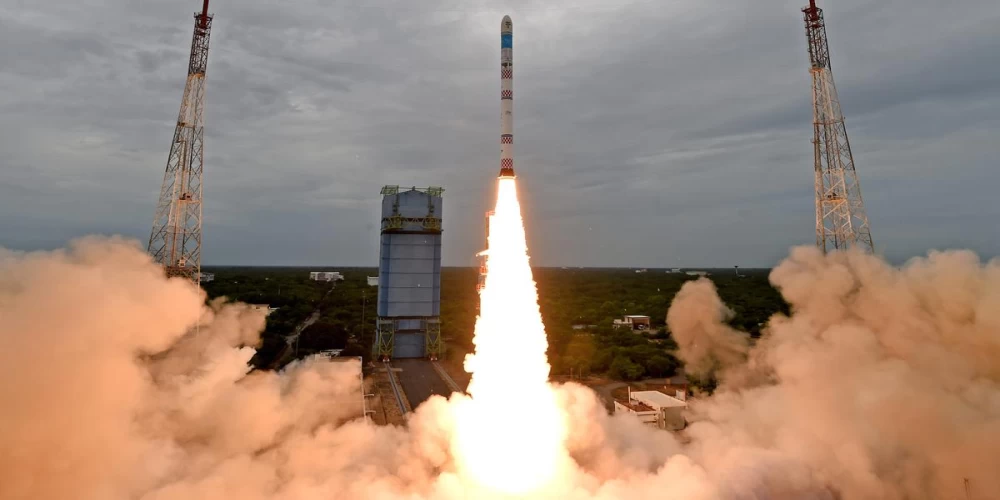
New Delhi: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched its latest Earth Observation Satellite, EOS-08, today at 9:17 AM from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota. The satellite was carried into orbit by the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV)-D3.
The EOS-08 mission aims to design and develop a microsatellite with advanced payload instruments, incorporating new technologies for future operational satellites. Built on the Microsat/IMS-1 bus, EOS-08 carries three key payloads: the Electro Optical Infrared Payload (EOIR), the Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry payload (GNSS-R), and the SiC UV Dosimeter.
The EOIR payload is designed to capture images in the Mid-Wave IR (MIR) and Long-Wave IR (LWIR) bands, both during the day and night. These images will be used for satellite-based surveillance, disaster monitoring, environmental observation, fire detection, volcanic activity monitoring, and industrial disaster assessment.
The GNSS-R payload will demonstrate the use of GNSS-R-based remote sensing for various applications, including ocean surface wind analysis, soil moisture assessment, flood detection, cryosphere studies in the Himalayan region, and inland waterbody monitoring. The SiC UV Dosimeter is tasked with monitoring UV irradiance on the Crew Module of the Gaganyaan Mission and will serve as a high-dose alarm sensor for gamma radiation.
EOS-08 will operate in a Circular Low Earth Orbit (LEO) at an altitude of 475 km with an inclination of 37.4°. The satellite has a mass of approximately 175.5 kg and a mission life of one year, generating power of around 420 W. It interfaces with the SSLV-D3 launch vehicle.
This mission represents a significant advancement in satellite mainframe systems, including the Integrated Avionics system, known as the Communication, Baseband, Storage, and Positioning (CBSP) Package. This package combines multiple functions into a single, efficient unit with cold redundant systems, using commercial off-the-shelf components. The satellite also features a structural panel embedded with a PCB, an embedded battery, a Micro-DGA (Dual Gimbal Antenna), an M-PAA (Phased Array Antenna), and a flexible solar panel for onboard technology demonstration.
The miniaturised design of the satellite's Antenna Pointing Mechanisms allows for a rotational speed of 6 degrees per second, with a pointing accuracy of ±1 degree. The miniaturised phased array antenna further enhances communication capabilities. The flexible solar panel, incorporating a foldable substrate and rigid end panel, improves power generation and structural integrity. A pyrolytic graphite sheet diffuser plate, known for its high thermal conductivity, reduces mass and is used in various satellite functions.
The EOS-08 mission also incorporates advanced technologies for X-band data transmission and an innovative battery management system. The mission’s indigenisation effort is reflected in its solar cell fabrication processes and the use of a Nano-Star Sensor for Microsat Applications. Additionally, the inertial system benefits from reaction wheel isolators, and a single antenna interface is used for TTC and SPS applications. Enhanced thermal management materials are employed to handle the thermal properties of the satellite’s components.
EOS-08's mission management is further improved by an auto-launch pad initialization feature, showcasing ISRO's commitment to innovative space technology. /BI